13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2016; 6(6):808-816. doi:10.7150/thno.13826 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Synthesis and Preclinical Evaluation of a Highly Improved Anticancer Prodrug Activated by Histone Deacetylases and Cathepsin L
1. Department of Molecular Genetics & Microbiology, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New York, USA;
2. Department of Chemistry, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New York, USA.
Abstract
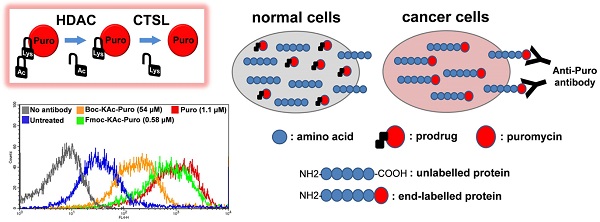
Lack of absolute selectivity against cancer cells is a major limitation for current cancer therapies. In the previous study, we developed a prodrug strategy for selective cancer therapy using a masked cytotoxic agent puromycin [Boc-Lys(Ac)-Puromycin], which can be sequentially activated by histone deacetylases (HDACs) and cathepsin L (CTSL) to kill cancer cells expressing high levels of both enzymes. Despite the promise as a selective cancer therapy, its requirement of relatively high dosage could be a potential issue in the clinical setting. To address this issue, we aimed to further improve the overall efficacy of our prodrug strategy. Since the proteolytic cleavage by CTSL is the rate-limiting step for the drug activation, we sought to improve the substrate structure for CTSL activity by modifying the α-amino protecting group of lysine. Here we show that protection with Fmoc [Fmoc-Lys(Ac)-Puromycin] exhibits a marked improvement in overall anticancer efficacy compared to the original Boc-Lys(Ac)-Puromycin and this is mainly due to the highly efficient cellular uptake besides its improved substrate structure. Furthermore, to address a concern that the improved drug efficacy might direct high toxicity to the normal cells, we confirmed that Fmoc-Lys(Ac)-Puromycin still retains excellent cancer selectivity in vitro and no obvious systemic off-target toxicity in vivo. Thus our preclinical evaluation data presented here demonstrate that the Fmoc-Lys(Ac)-Puromycin exhibits substantially improved anticancer efficacy, further supporting our approach for the selective cancer therapy.
Keywords: targeted therapy, prodrug, histone deacetylase, cathepsin L, drug development.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact