13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2016; 6(6):773-794. doi:10.7150/thno.14394 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Interleukin-6 Induced “Acute” Phenotypic Microenvironment Promotes Th1 Anti-Tumor Immunity in Cryo-Thermal Therapy Revealed By Shotgun and Parallel Reaction Monitoring Proteomics
1. Key Laboratory of Systems Biomedicine (MOE), Shanghai Center for Systems Biomedicine, the School of Biomedical Engineering and MED-X Research Institute, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
2. Institute for Systems Biology, Seattle, WA, USA.
Abstract
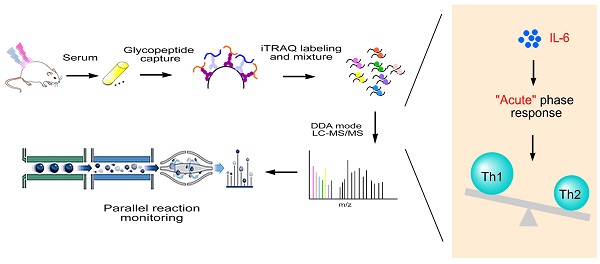
Cryo-thermal therapy has been emerged as a promising novel therapeutic strategy for advanced breast cancer, triggering higher incidence of tumor regression and enhanced remission of metastasis than routine treatments. To better understand its anti-tumor mechanism, we utilized a spontaneous metastatic mouse model and quantitative proteomics to compare N-glycoproteome changes in 94 serum samples with and without treatment. We quantified 231 highly confident N-glycosylated proteins using iTRAQ shotgun proteomics. Among them, 53 showed significantly discriminated regulatory patterns over the time course, in which the acute phase response emerged as the most enhanced pathway. The anti-tumor feature of the acute response was further investigated using parallel reaction monitoring target proteomics and flow cytometry on 23 of the 53 significant proteins. We found that cryo-thermal therapy reset the tumor chronic inflammation to an “acute” phenotype, with up-regulation of acute phase proteins including IL-6 as a key regulator. The IL-6 mediated “acute” phenotype transformed IL-4 and Treg-promoting ICOSL expression to Th1-promoting IFN-γ and IL-12 production, augmented complement system activation and CD86+MHCII+ dendritic cells maturation and enhanced the proliferation of Th1 memory cells. In addition, we found an increased production of tumor progression and metastatic inhibitory proteins under such “acute” environment, favoring the anti-metastatic effect. Moreover, cryo-thermal on tumors induced the strongest “acute” response compared to cryo/hyperthermia alone or cryo-thermal on healthy tissues, accompanying by the most pronounced anti-tumor immunological effect. In summary, we demonstrated that cryo-thermal therapy induced, IL-6 mediated “acute” microenvironment shifted the tumor chronic microenvironment from Th2 immunosuppressive and pro-tumorigenic to Th1 immunostimulatory and tumoricidal state. Moreover, the magnitude of “acute” and “danger” signals play a key role in determining the efficacy of anti-tumor activity.
Keywords: “acute” phase response, cryo-thermal therapy, interleukin-6, parallel reaction monitoring, Th1 anti-tumor immunity.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact