13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2016; 6(2):192-203. doi:10.7150/thno.13657 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Mono-arginine Cholesterol-based Small Lipid Nanoparticles as a Systemic siRNA Delivery Platform for Effective Cancer Therapy
1. † School of Life Science, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, 123 Cheomdangwagi-ro, Gwangju 500-712, Republic of Korea.
2. ‡ KAIST Institute for the BioCentury, Department of Biological Sciences, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and technology (KAIST), 291 Daehak-ro, Daejeon 305-701, Republic of Korea
Abstract
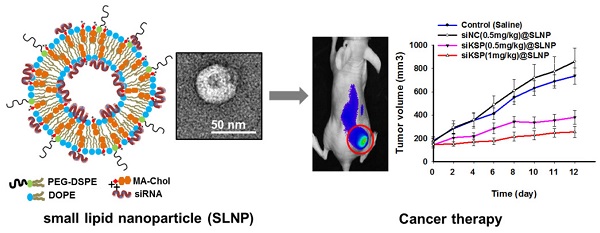
Although efforts have been made to develop a platform carrier for the delivery of RNAi therapeutics, systemic delivery of siRNA has shown only limited success in cancer therapy. Cationic lipid-based nanoparticles have been widely used for this purpose, but their toxicity and undesired liver uptake after systemic injection owing to their cationic surfaces have hampered further clinical translation. This study describes the development of neutral, small lipid nanoparticles (SLNPs) made of a nontoxic cationic cholesterol derivative, as a suitable carrier of systemic siRNA to treat cancers. The cationic cholesterol derivative, mono arginine-cholesterol (MA-Chol), was synthesized by directly attaching an arginine moiety to cholesterol via a cleavable ester bond. siRNA-loaded SLNPs (siRNA@SLNPs) were prepared using MA-Chol and a neutral helper lipid, dioleoyl phosphatidylethanolamine (DOPE), as major components and a small amount of PEGylated phospholipid mixed with siRNA. The resulting nanoparticles were less than ~50 nm in diameter with neutral zeta potential and much lower toxicity than typical cationic cholesterol (DC-Chol)-based lipid nanoparticles. SLNPs loaded with siRNA against kinesin spindle protein (siKSP@SLNPs) exhibited a high level of target gene knockdown in various cancer cell lines, as shown by measurement of KSP mRNA and cell death assays. Furthermore, systemic injection of siKSP@SLNPs into prostate tumor-bearing mice resulted in preferential accumulation of the delivered siRNA at the tumor site and significant inhibition of tumor growth, with little apparent toxicity, as shown by body weight measurements. These results suggest that these SLNPs may provide a systemic delivery platform for RNAi-based cancer therapy.
Keywords: cationic lipids · cancer therapy · drug delivery · nanoparticles · RNAi · siRNA
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact