13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2015; 5(2):196-205. doi:10.7150/thno.7976 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Percutaneous Intramyocardial Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Induces Superior Improvement in Regional Left Ventricular Function Compared with Bone Marrow Mononuclear Cells in Porcine Myocardial Infarcted Heart
1. Department of Cardiology, Xijing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an 710032, China;
2. Department of Cardiology, Chinese PLA General Hospital,Beijing 100853, China;
3. Department of Nuclear Medicine,Xijing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an 710032, China;
4. School of Life Science and Technology, Xidian University, Xi'an 710126, China.
* Contributed equally to the study.
Abstract
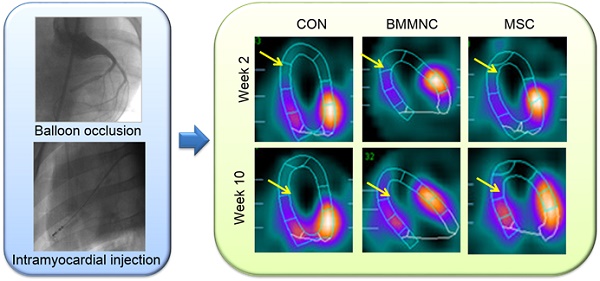
Aim: To investigate the efficacy and feasibility of percutaneous intramyocardial injection of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) and autologous bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells (BMMNC) on cardiac functional improvement in porcine myocardial infarcted hearts. Methods and Results: Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) was induced in 22 minipigs by temporary balloon occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery for 60min.Two weeks post AMI, BMMNC (n = 7, 245 ± 98×106), MSC (n = 8, 56 ± 17×106), or phosphate buffered saline (PBS; n = 7) were injected intramyocardially. Cardiac function and myocardial perfusion were analyzed by echocardiography and gated single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography (SPECT/CT) at 1 week before AMI and 2 and 10 weeks after AMI. Cell engraftment, proliferation, vascular density, and cardiac fibrosis were evaluated by histology analysis. In all groups, the echocardiography revealed no significant change in the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), left ventricular end-systolic volume (LVESV), or left ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) at 10 weeks after AMI compared with those at 2 weeks after AMI. However, the wall motion score index (WMSI) and left ventricular systolic wall thickening (WT%) were significantly improved at 10 weeks compared with those at 2 weeks after AMI in the MSC group (WMSI 1.55 ± 0.06 vs. 1.87 ± 0.10, WT 33.4 ± 2.3% vs.24.8 ± 2.7%,p < 0.05) but not in the BMMNC group. In addition, myocardial perfusion quantified by SPECT/CT was improved in both the MSC and BMMNC groups, whereas the MSC group showed a superior improvement in vascular density and collagen volume fraction (p < 0.05). Conclusion: This preclinically relevant study suggests that when delivered by percutaneous (transcatheter) intramyocardial injection, MSC might be more effective than BMMNC to improve ischemia and reperfusion after AMI.
Keywords: Angiogenesis, Imaging, Myocardial infarction, Remodeling, Stem cells.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact