13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2012; 2(6):577-588. doi:10.7150/thno.4443 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Monitoring Breast Tumor Lung Metastasis by U-SPECT-II/CT with an Integrin αvβ3-Targeted Radiotracer 99mTc-3P-RGD2
1. School of Health Sciences, Purdue University, IN 47907, USA.
2. Department of Nuclear Medicine, Nanjing First Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210006, China.
Received 2012-4-5; Accepted 2012-4-23; Published 2012-6-5
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the capability of u-SPECT-II/CT to monitor the progression of breast cancer lung metastasis using 99mTc-3P-RGD2 as a radiotracer.
Methods: The breast cancer lung metastasis model was established by tail-vein injection of 2 x 105 - 1.5 x 106 MDA-MB-231 cells into each athymic nude mouse. SPECT/CT studies were performed at a specified time after inoculation of MDA-MB-231 cells. Histological staining was used to further confirm the presence of lung metastases.
Results: We found that both inoculation time and tumor cell load had significant influence on the extent of lung metastasis. For example, if animals were injected with 2 x 105 MDA-MB-231 cells, there were no detectable metastatic breast tumors in the lungs after 8 weeks. If animals were injected with 1 x 106 MDA-MB-231 cells, there were many tumors in both lungs at week 8. When 1.5 x 106 MDA-MB-231 cells were injected, the animal became very weak by week 7. We also found a rare example of breast cancer metastasis in the muscle and mediastinal lymph nodes. The tumor necrotic regions were clearly delineated by u-SPECT-II/CT.
Conclusion: This study clearly demonstrated that 99mTc-3P-RGD2 is an excellent radiotracer for noninvasive imaging of metastatic breast tumors in the lungs, mediastinal lymph nodes and muscles. 99mTc-3P-RGD2 SPECT/CT is an outstanding platform for monitoring the progression of breast cancer lung metastases, semi-quantification of breast tumor load in the lungs and delineation of tumor necrosis in small animals.
Keywords: Breast Cancer Lung Metastasis, 99mTc-3P-RGD2, u-SPECT-II/CT.
Introduction
Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in women worldwide. Metastatic breast cancer is characterized by spreading cancer cells into nearby breast tissue, and other body parts (e.g. bone, lymph nodes, liver and lungs), and remains the main cause of death of breast cancer patients. As in many other metastatic cancer types, specific molecular changes occurring within tumor cells and the tumor microenvironment contribute to the detachment of tumor cells from the primary tumor mass, invasion into the tumor stroma, intravasation into nearby blood vessels or lymphatics, survival in the blood stream, extravasation into and colonization of the target organ, and finally, metastatic outgrowth [1-3].
Elucidation of molecular mechanisms underlying breast cancer metastasis has gained tremendously from small animal models [1]. The lung metastasis model is often established by the tail vein injection of breast cancer cells [4]. Although this model has been broadly used to evaluate new anticancer drugs [1], it is difficult to accurately monitor the therapy response. There are several noninvasive imaging modalities for monitoring therapy response in small animal metastasis models. These include optical imaging with bioluminescence or fluorescence [4-6], magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [7], positron emission tomography (PET) [8] and in vivo confocal analysis during tumor development in small animals [9]. MRI relies on anatomical changes during and after therapy while optical imaging methods have limitations in imaging small metastasis due to their low spatial resolution. 18F-FDG has been used for cancer diagnosis, staging and therapy monitoring [10]; but glucose metabolism may not be an ideal biomarker for treatment response due to its limited sensitivity in detecting small pulmonary metastatic lesions [11]. Therefore, it will be of great interest to develop an imaging tool to monitor the progression of breast cancer lung metastasis in a noninvasive fashion.
Angiogenesis is one of the key requirements for tumor growth and metastasis [12-14], and is regulated by proteins, such as angiogenesis inhibitors and integrins. Among the integrins identified and characterized so far, integrin αvβ3 is studied most extensively. Integrin αvβ3 is a receptor for extracellular matrix proteins with the exposed arginine-glycine-aspartic (RGD) tripeptide sequence. It is expressed at low levels on epithelial cells and mature endothelial cells, but is highly expressed in neuroblastomas, glioblastomas, melanomas, and carcinomas of the breast and lung [15-19]. The altered integrin αvβ3 expression has been detected in breast cancer [20-22], and correlated with an aggressive phenotype and metastatic dissemination [21, 22]. It was reported that integrin αvβ3 is over-expressed on both tumor cells and activated endothelial cells on the neovasculature of the breast cancer xenografts [23]. All these facts make integrin αvβ3 an interesting biomarker for noninvasive diagnosis of breast cancer and related metastasis by PET or SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography).
Radiolabeled cyclic RGD peptides are radiotracers targeting the integrin αvβ3 expressed on both tumor cells and tumor neovasculature [24-27]. [18F]Galacto-RGD and [18F]AH111585 are 18F-labeled cyclic RGD peptides, and are currently under clinical trials for noninvasive detection of tumors and related metastasis by PET in cancer patients [28-30]. It was found that the radiotracer tumor uptake correlated well with the integrin αvβ3 expression levels. A significant challenge for them to assume a wide-spread utility is their clinical availability at low cost. A phase I study was reported for 99mTc-NC100692, a 99mTc-labeled RGD peptide monomer [31]. Although clinical data showed that 99mTc-NC100692 was able to detect malignant lesions, the intensive liver uptake and hepatobiliary excretion will limit its continuing clinical applications. Therefore, there is an unmet medical need for more efficient radiotracers that are clinically useful for early detection of the integrin αvβ3-positive tumors and their related metastasis.
99mTc-3P-RGD2([99mTc(HYNIC-3P-RGD2)(tricine)(TPPTS)]: HYNIC = 6-hydrazinonicotinyl; 3P-RGD2 = PEG4-E[PEG4-c(RGDfK)]2; PEG4= 15-amino-4,7,10,13-tetraoxapentadecanoic acid; and TPPTS = trisodium triphenylphosphine-3,3',3''-trisulfonate) is a 99mTc-labeled cyclic RGD peptide dimer. In animal models, 99mTc-3P-RGD2 shows high tumor uptake, rapid renal clearance, and high metabolic stability [32, 33]. It is currently under clinical investigations as a SPECT radiotracer for imaging lung carcinomas [34]. Previously, we found that 99mTc-3P-RGD2 was useful for detection of αvβ3-postive tumors in small animals [32, 35], and its tumor uptake was correlated well to the integrin αvβ3 expression levels [35]. Recently, we found that 99mTc-3P-RGD2 SPECT/CT was useful for accurate quantification of the tumor radioactivity accumulation and delineation of necrotic regions [36]. The objective of this study was to evaluate the capability of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 SPECT/CT as a noninvasive imaging tool to monitor the progression of breast cancer lung metastasis.
Materials and Methods
Materials and Analytical Method. Trisodium triphenylphosphine-3,3',3''-trisulfonate (TPPTS) and tricine were purchased from Sigma/Aldrich (St. Louis, Missouri). HYNIC-3P-RGD2 (HYNIC = 6-(2-(2-sulfonato-benzaldehyde)hydrazono)nicotinyl; 3P-RGD2 = PEG4-E[PEG4-c(RGDfK)]2), and PEG4 = 15-amino-4,7,10,13-tetraoxapentadecanoic acid) was prepared using the literature method [32]. Na99mTcO4 was obtained from Cardinal HealthCare (Chicago, IL). The radio-HPLC method used a LabAlliance system equipped with a β-ram IN-US detector and Zorbax C18 column (4.6 mm x 250 mm, 300 Å pore size). The flow rate was 1 mL/min. The mobile phase was isocratic with 90% solvent A (25 mM NH4OAc buffer, pH = 5.0) and 10% solvent B (acetonitrile) at 0 - 5 min, followed by a gradient mobile phase from 10% B at 5 min to 40% B at 20 min.
Radiolabeling and Dose Preparation. 99mTc-3P-RGD2 was prepared according to literature method [32] using lyophilized kit formulation, which contains 20 μg HYNIC-3P-RGD2, 5 mg TPPTS, 6.5 mg tricine, 40 mg mannitol, 38.5 mg disodium succinate hexahydrate and 12.7 mg succinic acid. 99mTc-labeling was accomplished by adding 1 - 1.5 mL of Na99mTcO4 solution (1,110 - 1,850 MBq). The reconstituted vial was heated at 100 °C for 30 min. The resulting solution was analyzed by radio-HPLC. The radiochemical purity (Supplementary Material: Figure SI1) was >95% for all imaging studies. Doses were prepared by dissolving the radiotracer in saline to a concentration of 370 - 555 MBq/mL. Each animal was injected with ~0.1 mL (37 - 55 MBq/1.25 - 1.5 μg HYNIC-3P-RGD2) of the dose solution.
Animal Model. Animal studies were carried out in compliance with the NIH animal experiment guidelines (Principles of Laboratory Animal Care, NIH Publication no. 86-23, revised 1985). The animal protocol was approved by the Purdue University Animal Care and Use Committee (PACUC No. 04-014-2010). MDA-MB-231 cell line was obtained from ATCC (Manassas, VA). The MDA-MB-231 cells were cultured in the RPMI Medium 1640 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, ATCC) and 1% penicillin and streptomycin (GIBCO) solution at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 in air. Female athymic nu/nu mice at 4 - 5 weeks of age were purchased from Harlan (Indianapolis, IN). The lung metastasis model was established by injecting MDA-MB-231 cells into the tail vein of each animal. SPECT/CT studies were performed at the specified time after inoculation of tumor cells.
u-SPECT/CT. SPECT/CT images were obtained using a u-SPECT-II/CT scanner (Milabs, Utrecht, The Netherlands) equipped with a 0.6 mm multi-pinhole collimator. The tumor-bearing mouse was injected with 37 - 55.5 MBq of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 via the tail-vein. At 60 min post-injection (p.i.), the animal was placed into a shielded chamber connected to an isoflurane anesthesia unit (Univentor, Zejtun, Malta). Anesthesia was induced using an air flow rate of 350 mL/min and ~3.0% isoflurane. After induction of anesthesia, the animal was immediately placed supine on the scanning bed. The air flow rate was reduced to ~250 mL/min with ~2.0% isoflurane. Rectangular scan in regions of interest (ROIs) from both the SPECT and CT were selected based on orthogonal optical images provided by integrated webcams. After SPECT acquisition (75 projections over 30 min per frame, 2 frames), the animal was then translated into the attached CT and imaged using the 'normal' acquisition settings (2 degree intervals) at 45 kV and 500 μA. After imaging, the animal was allowed to recover in a lead-shielded cage.
Image Reconstruction and Data Processing. SPECT reconstruction was performed using a POSEM (pixelated ordered subsets by expectation maximization) algorithm with 6 iterations and 16 subsets. CT data were reconstructed using a cone-beam filtered back-projection algorithm (NRecon v1.6.3, Skyscan). After reconstruction, the SPECT and CT data were automatically co-registered according to the movement of robotic stage, and re-sampled to equivalent voxel sizes. Co-registered images were further rendered and visualized using the PMOD software (PMOD Technologies, Zurich, Switzerland). A 3D-Guassian filter (0.8 mm FWHM) was applied to smooth noise, and LUTs (look-up tables) were adjusted for good visual contrast. Reconstructed images were visualized as both orthogonal slices and maximum intensity projections.
Radioactivity Quantification. Radiation sources of known amount of radioactivity were imaged and reconstructed using the same scanning protocol described above. A standard curve (Supplementary Material: Figure SI2) was generated to correlate the pixel intensities in reconstructed images to the radioactivity measured by the γ-counter (Shelton, CT). The organ delineation was performed on SPECT/CT images. ROIs were drawn manually to cover entire organ in the transverse view of SPECT/CT image. The organ volume and radioactivity counts were generated using the PMOD software. The radioactivity in each organ was calculated according to the above mentioned standard curve (Supplementary Material: Figure SI2). The organ uptake was expressed as the percentage of injected dose (%ID) and percentage of injected dose per unit volume (%ID/cm3). For tumor necrosis quantification, the total tumor volume was determined by CT, and the volume of viable tumor was measured by SPECT. The difference between these two values represents the volume of necrotic tumor tissues. The percentage of tumor necrosis was calculated using the following equation: % necrosis = 100 x (the volume of necrotic tissue)/(total tumor volume). The tumor/necrosis (T/N) ratios were calculated by circling an area (~0.01cm3) of necrotic region with the lowest radioactivity accumulation and an equally sized area of viable tumor with high radioactivity accumulation.
Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining. All tissues of interest harvested from the tumor-bearing mice two days after SPECT/CT were fixed in 10% formalin. Bone tissues were decalcified with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) until they became soft. Tissues were embedded in paraffin. The 4 μm sections were de-paraffinized and re-hydrated. Tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin to study the morphology under microscope. Aperio's ImageScope Viewer (Vista, CA) was used to visualize the whole-slide scans and capture images.
Immunohistochemistry. Tumors were embedded in the OCT (optimal cutting temperature compound) solution immediately after removal, snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and then cut into 5 μm slices. After drying thoroughly at room temperature, the slides were fixed with ice-cold acetone for 10 min, and dried in the air for 20 min. The sections were blocked with 10% goat serum for 30 min at room temperature, and were incubated with the hamster anti-integrin β3 antibody (1:100, BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA) and rat anti-CD31 antibody (1:100, BD Biosciences) for 1 h at room temperature. After incubating with the Cy3-conjugated goat anti-hamster and fluorescein (FITC)-conjugated goat anti-rat secondary antibodies (1:100, Jackson ImmunoResearch Inc., West Grove, PA) and washing with PBS, the fluorescence was visualized with an Olympic BX51 fluorescence microscope (Olympus America Inc., Center Valley, PA). Quantitative analysis of the integrin β3 expression was performed after immunostaining of tumor tissues. All images were obtained under 100x magnification with the same exposure time. Brightness and contrast adjustments were made equally to all the images. The average area of positively stained β3 on cryostat sections from at least 15 randomly selected fields in each slide was calculated to assess the relative expression in the tumor tissues by the NIH ImageJ software. The relative β3 level was expressed as a percentage (%) of the total area, and the ratio of the integrin expression in viable region to necrotic region was calculated.
Statistical Analysis. All data were expressed as the means ± the standard deviation. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Newman-Keuls test for multiple comparisons. The level of significance was set at p < 0.05.
Results
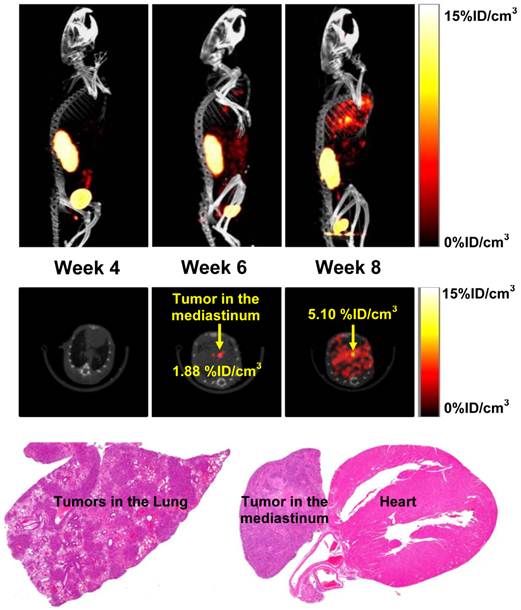
Monitoring Progression of Breast Cancer Lung Metastasis. Figure 1 shows the 3D and transverse views of SPECT/CT images of athymic nude mice (n = 8) with breast cancer lung metastasis. These images were obtained at week 4, 6 and 8 after tail-vein injection of 1.0 x 106 MDA-MB-231 cells to determine how long it takes to develop the measurable lung metastases in athymic nude mice. We found no metastatic breast tumor lesions detectable by u-SPECT/CT in the lungs at week 4 (Figure 1: top). By week 6, small breast cancer lesions started to appear in the mediastinum and lungs. At week 8, SPECT/CT images revealed many metastatic cancer lesions in both lungs while the tumor in mediastinal lymph nodes became larger. Histological data confirmed the presence of these metastatic lesions in the lungs and mediastinum (Figure 1: bottom), and were completely consistent with the results from SPECT/CT.
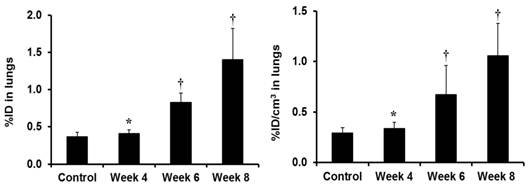
Figure 2 compares the %ID (left) and %ID/cm3 (right) uptake values of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 in the lungs. The tumor uptake values were calculated on the basis of SPECT/CT quantification in athymic nude mice (n = 8) at week 4, 6 and 8 after inoculation of 1.0 x 106 MDA-MB-231 cells. For comparison purposes, the animals (n = 4) without lung metastasis were used in the control group. Even though the lung uptake of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 (0.41 ± 0.05 %ID) at week 4 seemed to be higher than that in the control animals (0.36 ± 0.06 %ID), this difference was not significant (p > 0.05) within the experimental errors. At week 6, the tumor burden in the lungs became significant. The lung uptake of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 was much higher (0.89 ± 0.12 %ID; p < 0.01) than that in the control group. By week 8, the uptake of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 in the lungs was increased to 1.40 ± 0.42 %ID. In all cases, the lung size remained relatively unchanged (1.21 - 1.32 cm3) during the 8-week study period.
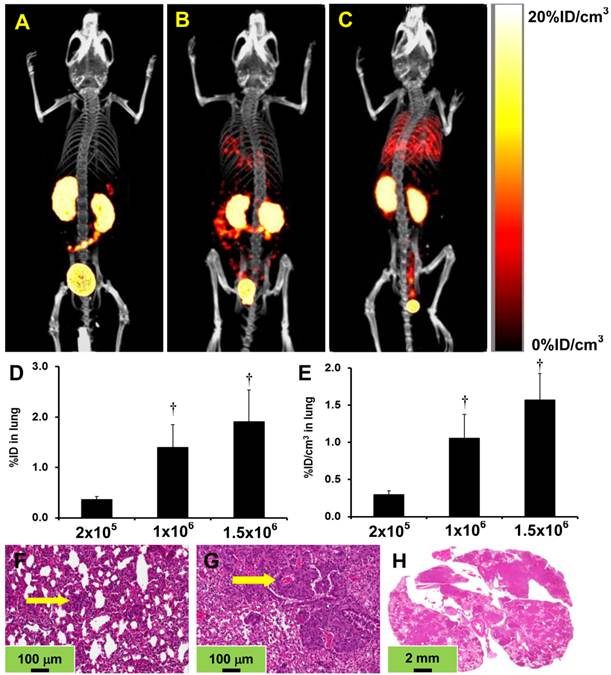
Tumor Cell Load on Progression of Breast Cancer Lung Metastasis. We examined the impact of tumor cell load on the extent of breast cancer lung metastasis by injecting different number of MDA-MB-231 cells. Figure 3 shows the 3D views of representative SPECT/CT images of the athymic nude mice after tail vein injection of 2 x 105 (A: n = 4), 1 x 106 (B: n = 8) and 1.5 x 106 (C: n = 4) of MDA-MB-231 cells. Obviously, the number of injected tumor cells had a significant impact on the extent of lung metastasis, which was consistent with the %ID (D) and %ID/cm3 (E) lung uptake values of 99mTc-3P-RGD2. For example, the animals injected with 2 x 105 of MDA-MB-231 cells showed no metastatic breast cancer lesions detectable by u-SPECT-II/CT in the lungs, lymph nodes and muscles 8 weeks after tumor cell inoculation. The lung uptake of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 was 0.40 ± 0.05 %ID as compared to 0.37 ± 0.05 %ID in the normal animals. However, histological data revealed many breast cancer micrometastases (Figure 3F), which were avascular and comprised of only several breast cancer cells. They are likely too small to be detected by u-SPECT-II/CT (detection limit: ~1 mm in diameter [36]). In contrast, the animals administered with 1 x 106 of MDA-MB-231 cells had many metastatic lesions in the lungs (Figure 3B) at week 8. The presence of metastatic breast cancer lesions was further confirmed by histological data (Figure 3G) of lung tissues and the increased lung uptake of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 (Figure 3D: 1.45 ± 0.45 %ID). When animals were administered with 1.5 x 106 of MDA-MB-231 cells, SPECT/CT imaging had to be performed at week 7 since it became very weak due to the reduced lung function. SPECT/CT images showed massive metastatic tumor lesions in lungs (Figure 3C), and the lung uptake of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 was increased to 1.91 ± 0.68 %ID (Figure 3D). Histological data were completely consistent with the presence of massive metastatic breast tumors (Figure 3H).
The 3D and transverse views of SPECT/CT images of an athymic nude mouse at week 4, 6 and 8 after tail-vein injection of 1.0 x 106 MDA-MB-231 cells, along with the H&E stained slices (magnification: 15×) of the lung and mediastinal tissues. Only one animal showed the presence of mediastinal tumors, as indicated by yellow arrows.
The %ID (left) and %ID/cm3 (right) uptake values of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 in the lungs obtained from SPECT/CT quantification in athymic nude mice (n = 8) at week 4, 6 and 8 after tail-vein injection of 1.0 x 106 MDA-MB-231 cells. Normal animals (n = 4) were used in the control group. †: p < 0.05, significantly different from the control group; *: p > 0.05, no significant difference from the control group.
Top: The 3D SPECT/CT images for athymic nude mice after the tail-vein injection of 2 x 105 (A: n = 4 at week 8), 1 x 106 (B: n = 8 at week 8) and 1.5 x 106 (C: n = 4 at week 7) MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Middle: The %ID (D) and %ID/cm3 (E) tumor uptake values of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 in the lungs obtained from SPECT/CT quantification. †: p < 0.01, significantly different from the group administered with 2 x 105 cells. Bottom: Representative H&E stained slices of lung tissues from animals injected with 2 x 105 (F: magnification = 200×), 1 x 106 (G: magnification = 200×) and 1.5 x 106 (H: magnification = 15×) cells. Arrows indicate the presence of metastatic breast tumors.
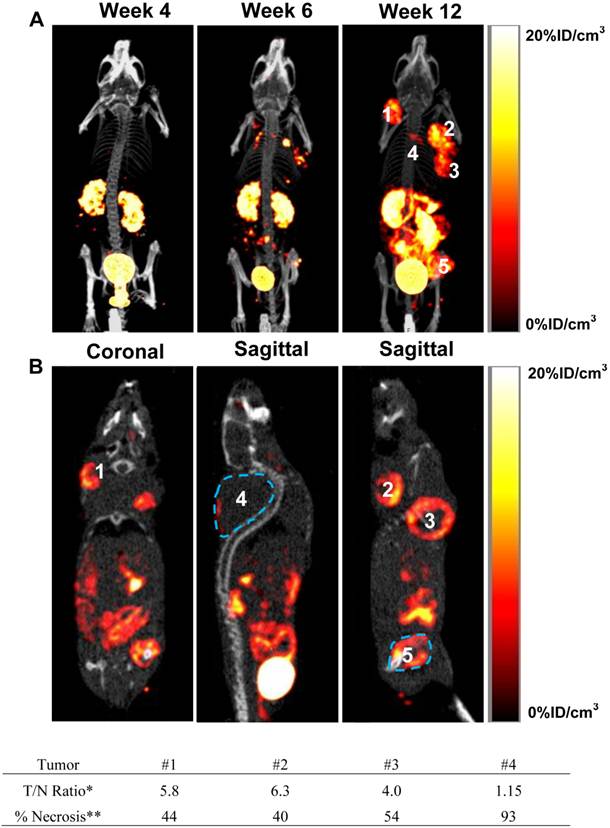
Breast Cancer Metastasis in Muscle and Bone. It is well-accepted that tail-vein injection of breast cancer cells leads to metastasis in lungs while intra-cardiac (left ventricle) injection of breast cancer cells often result in formation of metastases in the bone, brain and liver [1, 2, 37]. However, we found that the tail-vein injection of MDA-MB-231 cells could also result in breast cancer metastases in the muscle. Figure 4A illustrates the 3D views of SPECT/CT images of an athymic nude mouse at week 4, 6 and 12 after tail-vein injection of MDA-MB-231 cells. These images were obtained to show the progression of metastatic tumors over 12 weeks. Figure 4B exhibits the coronal and sagittal views of the SPECT/CT images obtained at week 12 to illustrate the relative location and characteristics of five different breast tumors (designated as #1 - #5). As expected, no metastatic breast cancer lesions were detectable at week 4. By week 6, there were several small metastatic breast tumors in the neck (#1), shoulder (#2), underarm (#3), back (#4) and hindlimb (#5). Since they were not seen in the SPECT/CT images of the same animal at week 4, we believe that they are true “hot spots” due to the αvβ3 binding of 99mTc-3P-RGD2. At week 12, the small breast cancer metastases became sizeable solid tumors. It was surprising that no breast cancer lesions were detectable by u-SPECT-II/CT in the lungs. The radioactivity accumulation in tumors #1 and #2 was relatively homogeneous (Figure 4B: coronal). The distribution of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 in tumor #3 was donut-shaped (not shell-shaped) with a large necrotic core (Figure 3B: sagittal). Tumor #4 is the largest (~1.2 g) among 5 metastatic breast tumors in this animal, but it had the least uptake of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 with the radioactivity accumulating only in a small portion of its outside edge (Figure 4B: sagittal) due to extensive necrosis. The metastatic lesion #5 was clearly seen in the muscle of left hindlimb (Figure 4B: sagittal). The volume of necrotic tissue was calculated by subtracting the volume of viable tumor (determined by SPECT) from the total tumor volume (measured by CT). The percentage of tumor necrosis was estimated to be 44, 40, 55 and 94 for tumors #1, #2, #3 and #4, respectively. The majority of tumor #4 was necrotic with little radioactivity accumulation. Their maximum tumor/necrosis (T/N) ratios were calculated to be 5.8, 6.3, 4.0 and 1.15, respectively. Because of the heterogeneity of tumor necrosis, these values should be used with caution.
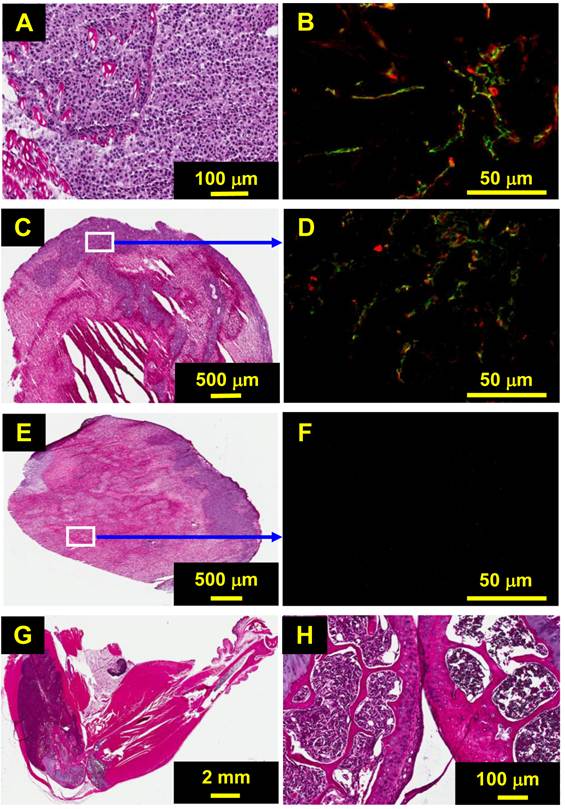
Figure 5 shows histological and immunohistochemical data for the selected metastatic breast tumor tissues. Tumors #1 and #2 were small (<0.4 cm3) with ~40% necrosis (Figure 5A). As a result, the integrin αvβ3 expression was relatively homogeneous in the tumor tissue (Figure 5B). The ratio of the integrin αvβ3 expression in the viable tissue to that in the necrotic region was ~6:1, which is close to that obtained from SPECT/CT (Figure 4). Tumor #3 had more necrosis (~55%), and integrin αvβ3 was expressed only on the outside edge of tumor tissue (Figure 5C). The integrin αvβ3 level in the viable region (Figure 5D) was similar to that in tumors #1 and #2 (Figure 4B). Likewise, the vasculature, as stained in CD31 (green), was rich in the viable region, which was similar to small tumors (Figure 5: B vs. D). Tumor #4 was also highly necrotic with little viable tumor tissue (Figure 5E). Immunohistochemical data also indicated that there was no CD31 and αvβ3 expression in the necrotic regions (Figure 5F), which is completely consistent with the low uptake of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 in tumor #4 (Figure 5B). Tumor #5 was in the muscle (Figure 5G) instead of bone. The breast tumor cells have already penetrated into the joint-bone and caused significant bone-resorption (Figure 5H).
Discussion
In this study, we found that u-SPECT-II/CT is a very useful tool to study the progression of breast cancer lung metastases. The resolution of u-SPECT-II/CT (< 0.5 mm) is higher than that obtained with bioluminescence and fluorescence [4-6]. We also found that 99mTc-3P-RGD2 SPECT/CT has the capability to quantify or semi-quantify the metastatic breast tumor load in the lungs (Figures 2 and 3), which is consistent with the results obtained from the glioma-bearing animal model [36]. These findings may have several important implications in both clinical practice and basic cancer research using small animal models. For example, 99mTc-3P-RGD2 SPECT/CT could be used as a screening tool to select appropriate cancer patients who would benefit most from anti-αvβ3 therapy. If the tumor in a patient has a high integrin αvβ3 expression anti-αvβ3 therapy would more likely be effective. If the tumor has little integrin αvβ3 expression, anti-αvβ3 therapy would not be effective regardless of the amount of anti-αvβ3 drug administered into patients. Another potential application is the utility of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 SPECT/CT for monitoring antiangiogenic therapy in small animal lung metastasis models by determining the tumor burden in lungs during and after treatment. If antiangiogenic therapy is effective, there would be a significantly reduced tumor burden in the lungs. As a result, the lung uptake of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 would be lower than that under the baseline conditions before therapy. If the antiangiogenic therapy is not effective, the tumor burden would be increased in the lungs. In this situation, the lung uptake of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 would be higher than that before therapy.
Two important factors (the inoculation time and the total number of breast tumor cells) have significant influence on the extent of metastasis in athymic nude mice. In general, more tumor cells injected into each animal will lead to the faster formation of more breast cancer lung metastases. If the animal is injected with 2 x 105 MDA-MB-231 cells, there are no detectable metastatic breast tumors in the lungs even 8 weeks after cell inoculation (Figure 3A) with the radioactivity accumulation comparable to that in the normal animals (Figure 3: D and E). When the animal is injected with 1 x 106 MDA-MB-231 cells, there are many metastatic breast tumor lesions at week 8 (Figure 3B) and the lung uptake of 99mTc-3P-RGD2 was significantly increased (Figure 3: D and E). If each animal is injected with 1.5 x 106 MDA-MB-231 cells, the animal becomes very weak by week 7 due to the reduced lung function caused by massive lung metastasis (Figure 3: C and H). As a result, the tumor load in the lungs was highest among three groups (Figure 3: D and E).
A: The 3D views of SPECT/CT images of an athymic nude mouse obtained at week 4, 6 and 12 after tail-vein injection of 1.0 x 106 MDA-MB-231 cells. B: Coronal and sagittal views of SPECT/CT images obtained at week 12 after tumor cell inoculation to illustrate the location of metastatic breast tumors in the neck (#1), back (#2 and #4), underarm (#3) and thigh (#5). *The tumor/necrosis ratio was calculated by circling an area (~0.01cm3) of necrotic region with the lowest radioactivity accumulation and an equally sized area of viable tumor with high radioactivity accumulation. **The percentage of tumor necrosis was estimated on the basis of total tumor volume determined by CT and the volume of viable tumor measured by SPECT.
A: Selected H&E staining data representing the metastatic breast tumors (#1 and #2) with ~40% necrosis. B: Representative overlay image of tumor slice stained with anti-integrin β3 (red color) or anti-CD31 (green color) antibody. Yellow color (red integrin β3 staining merged with green CD31 staining) indicates the presence of integrin αvβ3 on tumor neovasculature. C: Selected H&E staining data for tumor #3 (only half of the whole tumor tissue). D: The overlay image of tumor slice in the viable region stained with anti-integrin β3 (red) or anti-CD31 (green) antibody. E: H&E staining data for tumor #4 with extensive necrosis and little viable tumor tissue on the upper right edge. F: The overlay image of tumor slice in the necrotic tumor tissue stained with anti-integrin β3 (red) or anti-CD31 (green) antibody. G: Selected H&E staining data for tumor #5 in the left limb. H: Expanded region between two joint-bones. The tumor cells have penetrated into the joint-bone, but the tumor tissue remains largely in the muscle instead of inside the bone.
It is important to note that the lack of metastatic lung lesions in the SPECT/CT images does not necessarily always mean “no metastasis”. In experimental models of metastasis, it is not uncommon to find that there are no visible metastases in the lungs, but histological data reveals micrometastases consisting of many small tumor colonies [37]. As illustrated in Figure 3F, there are indeed many breast cancer lung micrometastases. Therefore, histological analysis must be used to further confirm the results obtained from the SPECT/CT studies. It is also important to emphasize that the occurrence of metastasis in the bone, mediastinum and muscle is not common if MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells are injected via the tail-vein. In this study, only one animal (1 out of 17 animals) had metastatic breast cancer lesions in mediastinum and one animal (1 out of 17 animals) had intramuscular and bone metastases. The remaining 15 animals all developed breast cancer lung metastases under the conditions used in this study.
MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells have high expression of integrin αvβ3 (Supplementary Material: Figure SI3), which strongly promotes metastasis by enhancing interactions between circulating tumor cells and platelets and promoting tumor cell arrest in the vasculature [38]. The integrin αvβ3 also supports the tumor cell interaction with platelets and leukocytes during blood flow, which results in shear resistant, and tumor cell arrest [38]. The integrin αvβ3 expression on circulating tumor cells in a constitutively activated functional form or in a state that allows rapid activation under blood flow conditions provides advantages for breast cancer metastasis. When MDA-MB-231 cells are injected from the tail vein, they are often trapped in pulmonary capillaries. Small intrapulmonary nodules are formed as “tumor cell clusters” or micrometastases, which may subsequently spread into mediastinal lymph nodes. Thus, it is not unexpected that small breast cancer lesions are detected in the mediastinum by u-SPECT/CT (Figure 1) at week 6.
Breast cancer has a propensity to metastasize to bone, lymph nodes, lung, liver, and (rarely) adrenal glands [1, 2]. In this study, we showed a rare case of muscle metastasis (Figure 4A), as indicated by the presence of many muscle cells within tumors #1 and #2 (Figure 4A). It is interesting to note that intramuscular breast cancer metastasis is rarely reported in preclinical tumor-bearing animal models. Although the exact mechanism is not clear, it is possible that the injected breast tumor cells cross the lungs without staying, and enter the left atrium. Tumor cells then circulate in the blood stream, and are finally trapped in intramuscular microvessels. These breast tumor cells may eventually develop into measurable solid tumors in the muscle.
Tumor necrosis is caused by rapid tumor growth and slow angiogenesis. Deficient blood supply results in tumor cell death and tissue necrosis [39]. It has been found that the breast tumors with necrosis were associated with their poor prognosis [40]. Imaging spontaneous necrosis in tumor tissues and the tumor necrosis developed after chemotherapy, radiation therapy or combination thereof have significant impact on the management of cancer patients [41]. In this study, we show that 99mTc-3P-RGD2 SPECT/CT is useful to identify the integrin αvβ3-negative necrotic regions. The pattern of necrosis can be different substantially among the tumors from the same animal (Figure 4: C and E). For example, the radioactivity distribution in tumor #3 is donut-shaped with a large necrotic core (Figure 4B) while the radioactivity in tumor #4 accumulates only in a small portion of its outside edge because of extensive necrosis. It must be noted that quantification of tumor necrosis is not an easy task. There are many necrotic regions in each tumor even if it is from the same animal. Each tumor slice in the SPECT/CT image is different and each area in that specific slice is also different with respect to the radiotracer tumor uptake and integrin αvβ3 expression levels. Thus, the % tumor necrosis and maximal T/N ratios were estimated to illustrate the relative radioactivity accumulation in tumors with necrosis.
Conclusion
In this study, we found that the tail-vein injection of MDA-MB-231 cells into each athymic nude mouse will generally lead to lung metastasis; but it may also result in metastasis in the mediastinal lymph nodes and muscles. It takes 6 - 8 weeks to develop metastatic lesions (≥1 mm) in the lungs if the animal is injected with 1 x 106 MDA-MB-231 cells. We clearly demonstrate that 99mTc-3P-RGD2 is an excellent radiotracer for noninvasive imaging of metastatic breast tumors in the lungs, mediastinal lymph nodes and muscles. 99mTc-3P-RGD2 SPECT/CT is an outstanding platform for monitoring the progression of breast cancer lung metastases, semi-quantification of the metastatic tumor burden in the lungs and delineation of tumor necrosis in small animals. 99mTc-3P-RGD2 SPECT/CT may have clinical applications for noninvasive monitoring of the response to chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy.
Supplementary Material
Fig.SI1 - Fig.SI3.
Acknowledgements
Authors would thank Dr. Aaron B. Taylor for his technical assistance in SPECT/CT studies, and Purdue University for the purchase of the u-SPECT-II/CT scanner (Milabs, Utrecht, The Netherlands). This work was supported by Purdue University and research grants: R01 CA115883 (S.L.) from the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and KG111333 (Y.Z. and S.L.) from the Susan G. Komen Breast Cancer Foundation.
Abbreviation
CT: computer tomography; EDTA: ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid; FBS: fetal bovine serum; FDG: 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose; [18F]Galacto-RGD: 2-[18F]fluoropropanamide c(RGDfK(SAA); SAA: 7-amino-L-glyero-L-galacto-2,6-anhydro-7-deoxyheptanamide; FITC: fluorescein; H&E: hematoxylin and eosin; HPLC: high performance liquid chromatography; LUT: look-up table; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; PET: positron emission tomography; POSEM: pixelated ordered subsets by expectation maximization; RCP: radiochemical purity; RGD: arginine-glycine-aspartic; ROI: region of interest; SPECT: single photon emission computed tomography.
Competing Interests
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
References
1. Fantozzi A, Christofori G. Mouse models of breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2006;8:212-222
2. Kim IS, Baek SH. Mouse models for breast cancer metastasis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;394:443-447
3. Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:563-572
4. Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu W, Giri DD, Viale A, Olshen AB, Gerald WL, Massagué J. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature. 2005;436:518-524
5. Kaijzel EL, van der Pluijm G, Löwik CW. Whole-body optical imaging in animal models to assess cancer development and progression. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:3490-3497
6. Minn AJ, Kang Y, Serganova I, Gupta GP, Giri DD, Doubrovin M, Ponomarev V, Gerald WL, Blasberg R, Massagué J. Distinct organ-specific metastatic potential of individual breast cancer cells and primary tumors. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:44-55
7. Zhao D, Richer E, Antich PP, Mason RP. Antivascular effects of combretastatin A4 phosphate in breast cancer xenograft assessed using dynamic bioluminescence imaging and confirmed by MRI. FASEB J. 2008;22:2445-2451
8. Kramer-Marek G, Kiesewetter DO, Capala J. Changes in HER2 expression in breast cancer xenografts after therapy can be quantified using PET and 18F-labeled affibody molecules. J Nucl Med. 2009;50:1131-1139
9. Gonda K, Watanabe TM, Ohuchi N, Higuchi H. In vivo nano-imaging of membrane dynamics in metastatic tumor cells using quantum dots. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:2750-2757
10. Lee JH, Rosen EL, Mankoff DA. The role of radiotracer imaging in the diagnosis and management of patients with breast cancer: part 2-response to therapy, other indications, and future directions. J Nucl Med. 2009;50:738-748
11. Bestic JM, Peterson JJ, Bancroft LW. Use of FDG PET in staging, restaging, and assessment of therapy response in Ewing sarcoma. RadioGraphics. 2009;29:1487-1501
12. Brooks PC, Clark RA, Cheresh DA. Requirement of vascular integrin αvβ3 for angiogenesis. Science. 1994;264:569-571
13. Desgrosellier JS, Cheresh DA. Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:9-22
14. Felding-Habermann B, O'Toole TE, Smith JW, Fransvea E, Ruggeri ZM, Ginsberg MH, Hughes PE, Pampori N, Shattil SJ, Saven A, Mueller BM. Integrin activation controls metastasis in human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:1853-1858
15. Bello L, Francolini M, Marthyn P, Zhang J, Carroll RS, Nikas DC, Strasser JF, Villani R, Cheresh DA, Black PM. αvβ3 and αvβ5 integrin expression in glioma periphery. Neurosurgery. 2001;49:380-389
16. Smythe WR, LeBel E, Bavaria JE, Kaiser LR, Albelda SM. Integrin expression in non-small cell carcinoma of the lung. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1995;14:229-239
17. Meitar D, Crawford SE, Rademaker AW, Cohn SL. Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastatic disease, N-myc-amplification, and poor outcome in human neuroblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14:405-414
18. Natali PG, Hamby CV, Felding-Habermann B, Liang B, Nicotra MR, Di Filippo F, Giannarelli D, Temponi M, Ferrone S. Clinical significance of αvβ3 integrin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in cutaneous malignant melanoma lesions. Cancer Res. 1997;57:1554-1560
19. Sengupta S, Chattopadhyay N, Mitra A, Ray S, Dasgupta S, Chatterjee A. Role of αvβ3 integrin receptors in breast tumor. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2001;20:585-590
20. Havaki S, Kouloukoussa M, Amawi K, osos Y, Arvanitis LD, Goutas N, Vlachodimitropoulos D, Vassilaros SD, Katsantoni EZ, Voloudakis-Baltatzis I, Aleporou-Marinou V, Kittas C, Marinos E. Altered expression pattern of integrin αvβ3 correlates with actin cytoskeleton in primary cultures of human breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2007;7:16-26
21. Sloan EK, Pouliot N, Stanley KL, Chia J, Moseley JM, Hards DK, Anderson RL. Tumor-specific expression of αvβ3 integrin promotes spontaneous metastasis of breast cancer to bone. Breast Cancer Res. 2006;8:R20
22. Pécheur I, Peyruchaud O, Serre CM, Guglielmi J, Voland C, Bourre F, Margue C, Cohen-Solal M, Buffet A, Kieffer N, Clézardin P. Integrin αvβ3 expression confers on tumor cells a greater propensity to metastasize to bone. FASEB J. 2002;16:1266-1268
23. Zitzmann S, Ehemann V, Schwab M. Arginine-Glycine-Aspartic acid (RGD)-peptide binds to both tumor and tumor endothelial cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 2002;62:5139-5143
24. Liu S. Radiolabeled cyclic RGD peptides as integrin αvβ3-targeted radiotracers: maximizing binding affinity via bivalency. Bioconjug Chem. 2009;20:2199-2213
25. Zhou Y, Chakraborty S, Liu S. Radiolabeled cyclic RGD peptides as radiotracers for imaging tumors and thrombosis by SPECT. Theranostics. 2011;1:58-82
26. Liu Z, Fan Wang F, Chen X. Integrin targeted delivery of radiotherapeutics. Theranostics. 2011;1:201-210
27. Cai W, Chen X. Multimodality molecular imaging of tumor angiogenesis. Nucl Med. 2008;49:113S-128S
28. Haubner R, Weber WA, Beer AJ, Vabuliene E, Reim D, Sarbia M, Becker KF, Goebel M, Hein R, Wester HJ, Kessler H, Schwaiger M. Noninvasive visualization of the activiated αvβ3 integrin in cancer patients by positron emission tomography and [18F]Galacto-RGD. PLoS Med. 2005;2:e70
29. Beer AJ, Niemeyer M, Carlsen J, Sarbia M, Nährig J, Watzlowik P, Wester HJ, Harbeck N, Schwaiger M. Patterns of αvβ3 expression in primary and metastatic human breast cancer as shown by 18F-Galacto-RGD PET. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:255-259
30. Kenny LM, Coombes RC, Oulie I, Contractor KB, Miller M, Spinks TJ, McParland B, Cohen PS, Hui AM, Palmieri C, Osman S, Glaser M, Turton D, Al-Nahhas A, Aboagye EO. Phase I trial of the positron-emitting Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptide radioligand 18F-AH111585 in breast cancer patients. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:879-886
31. Bach-Gansmo T, Danielsson R, Saracco A, Wilczek B, Bogsrud TV, Fangberget A, Tangerud A, Tobin D. Integrin receptor imaging of breast cancer: a proof-of-concept study to evaluate 99mTc-NC100692. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:1434-1439
32. Wang L, Shi J, Kim YS, Zhai S, Jia B, Zhao H, Liu Z, Wang F, Chen X, Liu S. Improving tumor targeting capability and pharmacokinetics of 99mTc-labeled cyclic RGD dimers with PEG4 linkers. Mol Pharm. 2009;6:231-245
33. Jia B, Liu Z, Zhu Z, Shi J, Jin X, Zhao H, Li F, Liu S, Wang F. Blood clearance kinetics, biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of a kit-formulated integrin αvβ3-selective radiotracer 99mTc-3PRGD2 in non-human primates. Mol Imaging Biol. 2010;13:730-736
34. Ma Q, Ji B, Jia B, Gao S, Ji T, Wang X, Han Z, Zhao G. Differential diagnosis of solitary pulmonary nodules using 99mTc-3P4-RGD2 scintigraphy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38:2145-2152
35. Zhou Y, Kim YS, Chakraborty S, Shi J, Gao H, Liu S. 99mTc-labeled cyclic RGD peptides for noninvasive monitoring of tumor integrin αvβ3 expression. Mol Imaging. 2011;10:386-397
36. Shao G, Zhou Y, Wang F, Liu S. Monitoring glioma growth and tumor necrosis with u-SPECT-II/CT by targeting integrin αvβ3. Mol Imaging. 2012 accepted
37. Zetter BR. Angiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Annu Rev Med. 1998;49:407-424
38. Gay LJ, Felding-Habermann B. Contribution of platelets to tumor metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:123-134
39. Jain RK. Determinants of tumor blood flow: a review. Cancer Res. 1988;48:2641-2658
40. Tomes L, Emberley E, Niu Y, Troup S, Pastorek J, Strange K, Harris A, Watson PH. Necrosis and hypoxia in invasive breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003;81:61-69
41. Richards CH, Mohammed Z, Qayyum T, Horgan PG, McMillan DC. The prognostic value of histological tumor necrosis in solid organ malignant disease: a systematic review. Future Oncol. 2011;7:1223-1235
Author contact
![]() Corresponding author: Dr. Shuang Liu, School of Health Sciences, Purdue University, 550 Stadium Mall Drive, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907. Phone: 765-494-0236; Fax 765-496-1377; Email: liu100purdue.edu
Corresponding author: Dr. Shuang Liu, School of Health Sciences, Purdue University, 550 Stadium Mall Drive, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907. Phone: 765-494-0236; Fax 765-496-1377; Email: liu100purdue.edu
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact